Tibial osteotomy, a type of knee surgery, is a crucial procedure aimed at realigning and stabilizing the knee joint. For individuals experiencing issues with knee stability and mobility, understanding the benefits and details of tibial osteotomy can be essential to making informed healthcare decisions.
What is Tibial Osteotomy?
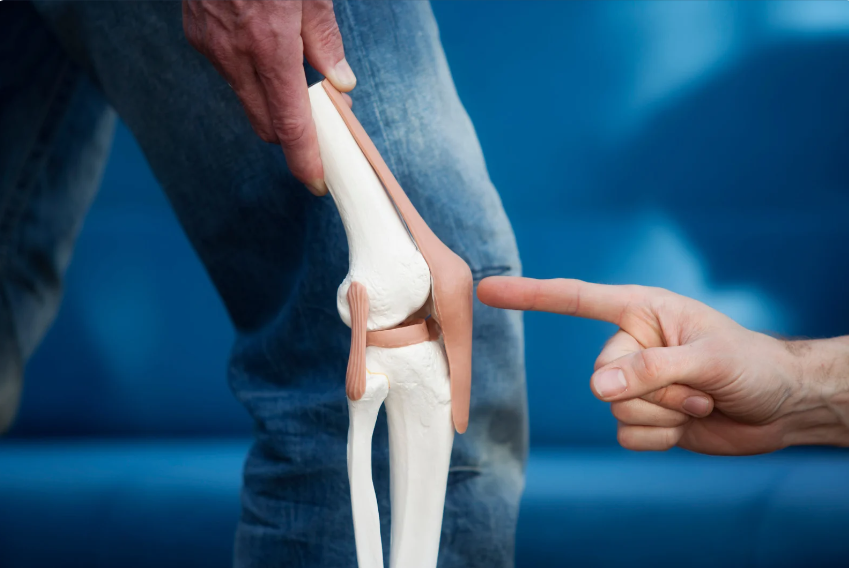
Tibial osteotomy, a form of knee surgery, involves realigning the tibia (shinbone) to redistribute weight and alleviate pressure on the damaged part of the knee joint. This procedure is commonly used to treat conditions like knee osteoarthritis and meniscal injuries, where joint misalignment contributes to pain and reduced mobility.
Conditions Treated with Tibial Osteotomy
Knee surgery, specifically tibial osteotomy, is often recommended for individuals with progressive knee osteoarthritis or those who have experienced a meniscal tear. Symptoms such as persistent knee pain, swelling, and difficulty performing daily activities may indicate a need for this procedure. Tibial osteotomy offers a proactive approach to joint health, potentially delaying or preventing the need for more invasive surgeries like knee replacement.
Benefits of Tibial Osteotomy
One of the primary benefits of knee surgery, tibial osteotomy, is the improvement in joint alignment and stability. By correcting the tibial angle, the procedure helps distribute weight more evenly across the knee joint, thereby reducing strain and discomfort. Enhanced mobility and range of motion are also significant benefits, allowing patients to regain functionality in their daily lives and activities.
Procedure Details
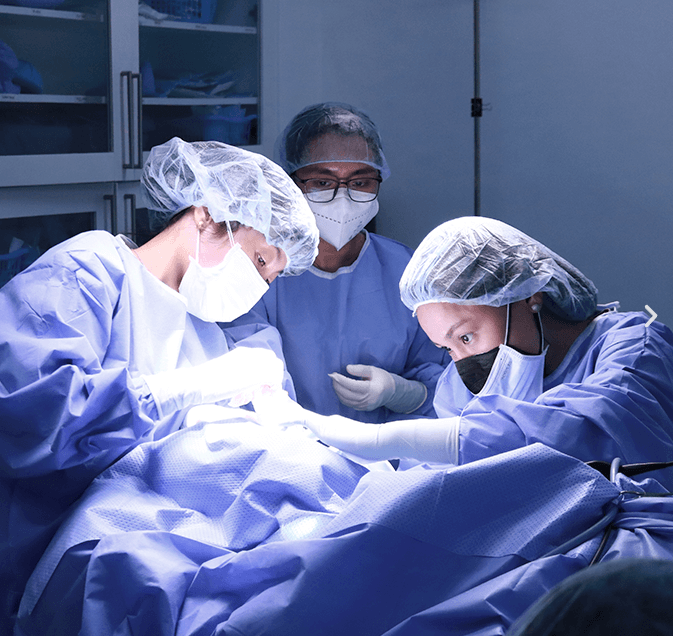
Before knee surgery, thorough pre-operative assessments, including imaging studies and physical evaluations, are conducted to determine the patient’s suitability for tibial osteotomy. During the procedure, the surgeon makes precise cuts in the tibia to realign the bone. Various techniques, such as medial opening wedge or lateral closing wedge osteotomy, may be employed based on the patient’s specific needs and the severity of knee misalignment. Although knee surgery, tibial osteotomy, is generally considered safe, potential risks include infection, blood clots, and nerve damage.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following knee surgery, tibial osteotomy, patients typically undergo a period of post-operative care in the hospital to monitor their initial recovery and manage pain. Rehabilitation focuses on strengthening the knee through targeted exercises and physical therapy to facilitate healing and restore function. The timeline for knee surgery, tibial osteotomy, recovery varies depending on individual factors, but most patients can expect gradual improvement and return to normal activities within several months.
Takeaway
Knee surgery, tibial osteotomy, is a valuable option for individuals seeking to improve knee stability and mobility. By addressing underlying joint alignment issues, this procedure can significantly enhance quality of life and reduce pain associated with knee osteoarthritis and other conditions. If you or someone you know is experiencing persistent knee problems, consulting with a healthcare professional about tibial osteotomy may offer a path to better joint health and functional recovery.