Shoulder injuries are among the most common musculoskeletal problems, often leading to significant pain and functional loss. The shoulders are the most movable joints in the human body, making them susceptible to injuries. Whether from repetitive stress at work or during sports activities, shoulder injuries can vary in severity and type. Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for effective recovery and returning to normal activities.
Common Types of Shoulder Injuries
Rotator Cuff Tears: Rotator cuff tears are one of the most prevalent shoulder injuries. They can occur due to two main causes: acute injuries, often resulting from sudden trauma, and degenerative tears, which develop gradually over time as tendons wear down. Symptoms typically include a dull ache in the shoulder, difficulty lifting the arm, and weakness. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital for effective treatment.
Tendinitis: Tendinitis is characterized by inflammation of the shoulder tendon, commonly caused by overuse due to laborious jobs or repetitive overhead activities in sports. Individuals may experience swelling, pain during movement, and tenderness around the shoulder joint. Proper rest, rehabilitation, and adjustments to activity levels are essential for recovery.
Dislocations: A dislocated shoulder occurs when the humeral head is displaced from its socket, typically resulting from a fall or direct impact. Glenohumeral dislocations often involve soft tissue injuries, such as rotator cuff tears or tears of the glenohumeral ligament. Symptoms include intense pain, swelling, and a visible deformity of the shoulder.
Arthritis: Arthritis can significantly impact shoulder functionality. There are two main forms: osteoarthritis, which usually occurs due to aging or repetitive use, leading to the deterioration of cartilage, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition that attacks the membranes surrounding the shoulder joint. Both types can cause severe pain and stiffness.
Impingement Syndrome: Shoulder impingement syndrome occurs when there is mechanical compression of the subacromial structures, such as the rotator cuff tendons and bursa, during arm elevation. Symptoms include pain and a limited range of motion, especially when lifting the arm above shoulder height. This condition often results from repetitive overhead movements and poor shoulder mechanics.
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder): Frozen shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, is a painful condition characterized by restricted active and passive range of motion in the shoulder. It usually develops slowly, leading to stiffness and pain that severely limits movement. Early intervention is crucial for effective treatment and rehabilitation.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Injuries
Accurate diagnosis of shoulder injuries is vital for effective treatment. Healthcare providers typically conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the patient’s history and symptoms. Imaging techniques, such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds, may also be employed to identify the extent of injuries and develop a suitable treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Injuries
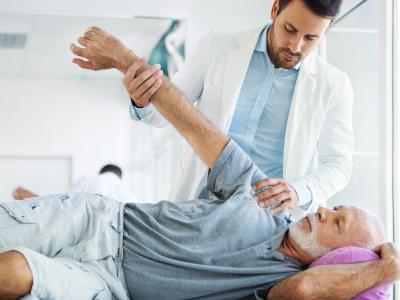
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is often the first line of treatment for many shoulder injuries. It focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and function through tailored exercises and manual therapy. Research shows that physical therapy can produce results comparable to surgical interventions, especially for non-traumatic rotator cuff tears. Patients can expect to engage in a variety of techniques, including stretching, strengthening exercises, and functional training.
Medication and Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are commonly used to manage shoulder pain. In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications or recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Proper pain management is crucial for enabling patients to engage in rehabilitation activities.
Surgical Interventions: When conservative treatments fail or in cases of severe injuries, surgical options may be necessary. Common surgical procedures include arthroscopy, where small incisions are made to repair damaged tissues, and open repair for more extensive injuries. A thorough discussion with a healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate surgical approach based on the individual’s condition.
Alternative Therapies: In addition to traditional treatments, alternative therapies such as acupuncture and chiropractic care may provide additional relief for shoulder pain. Some patients report significant improvements in pain and function with these methods. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative therapies.
Prevention of Shoulder Injuries
Preventing shoulder injuries is crucial for maintaining long-term shoulder health. Implementing proper ergonomics, avoiding repetitive strain, and incorporating strength and flexibility training can significantly reduce the risk of injuries. Additionally, warming up properly before engaging in sports or strenuous activities is essential for preventing acute injuries.
Takeaway
Timely Shoulder Injuries Treatment is essential for recovery and maintaining a high quality of life. Whether through physical therapy, medication, or surgical intervention, individuals should seek professional help when experiencing shoulder pain. Understanding the various types of shoulder injuries and their treatments can empower patients to make informed decisions about their care.