Understanding Non-Healing Wounds
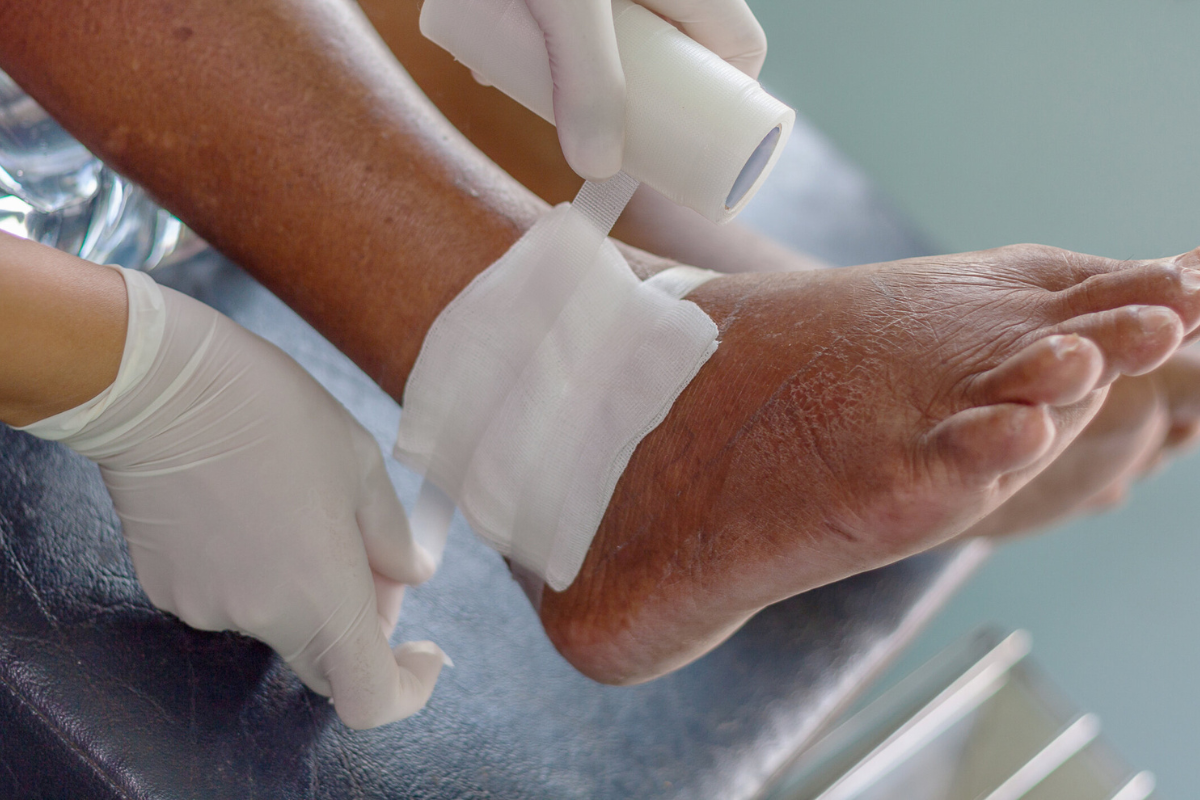
Non-healing wounds are those that fail to progress through the normal stages of recovery within an expected timeframe. Typically, wounds should close and repair within weeks, but some linger for months due to underlying medical or structural issues. Conditions like diabetes, poor circulation, persistent infections, and trauma often contribute to chronic wounds. Unlike minor cuts or surgical incisions that heal steadily, non-healing wounds remain open, creating risks of infection and functional impairment. Orthopedic complications add another layer of concern, especially when bones, joints, or supporting tissues are exposed or damaged. Patients with untreated chronic wounds often face reduced mobility, pain, and even systemic health risks. Recognizing the signs early and seeking specialized care helps prevent the worsening of these conditions.
Why Orthopedic Specialists Are Involved in Wound Care
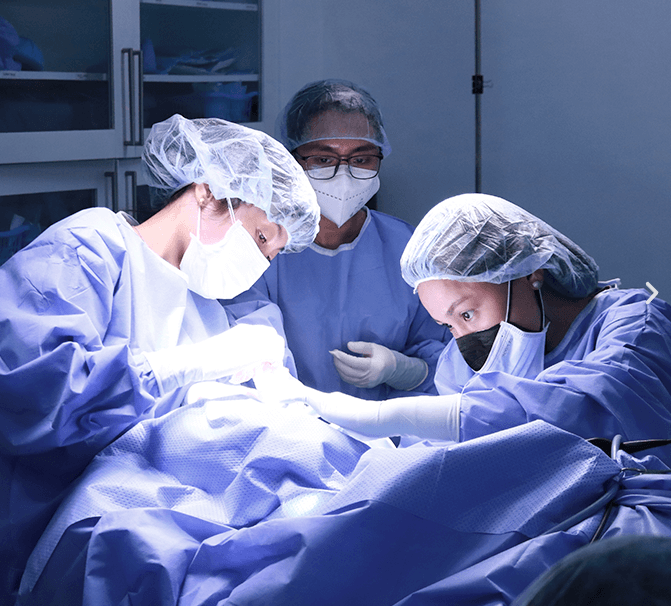
Orthopedic doctors play a unique role when wounds affect structures beneath the skin. While general wound care can address superficial injuries, complex wounds that involve bones, tendons, or joints require orthopedic expertise. These specialists understand the musculoskeletal system, allowing them to identify hidden damage that may hinder healing. For example, a wound that exposes bone or cartilage demands different treatment compared to a surface-level injury. Orthopedic specialists also coordinate with wound care teams, vascular surgeons, and infectious disease experts to manage multifaceted cases. Their involvement becomes especially crucial when wounds stem from fractures, surgical complications, or diabetic foot problems that threaten mobility. By treating both the wound and the underlying orthopedic issue, specialists increase the chance of long-term recovery. This dual approach reduces risks of amputation or chronic disability, offering patients a better quality of life.
Advanced Orthopedic Treatment Approaches
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds relies on both surgical and non-surgical techniques. One common procedure is surgical debridement, which removes dead tissue to encourage the body’s natural healing response. In more severe cases, skin grafts or flap procedures cover exposed bone or deep wounds, providing a fresh blood supply to aid repair. For wounds linked to fractures, orthopedic fixation devices such as plates, screws, or external frames may be required to stabilize bones and promote healing. Advanced biologic therapies, including growth factors and bioengineered dressings, are increasingly used to accelerate tissue regeneration. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is another supportive treatment that enhances oxygen supply, crucial for healing stubborn wounds. These methods are often tailored to each patient’s condition, taking into account the location, severity, and underlying health problems. By combining modern technology with surgical expertise, orthopedic specialists create a comprehensive care plan that addresses both immediate and long-term healing.
Orthopedic Management of Infection in Wounds
One of the greatest threats to wound healing is infection, especially when bacteria spread to the bone, leading to osteomyelitis. Orthopedic surgeons are trained to identify and treat infections that standard wound care may not resolve. They may perform surgical cleaning, known as irrigation and debridement, to eliminate infected tissue and restore a healthy environment for healing. In cases where bone is affected, stabilizing the structure becomes critical to avoid deformities or long-term disability. Systemic antibiotics are commonly prescribed, but orthopedic specialists may also apply local antibiotics directly into the wound site for targeted effectiveness. For severe infections, multiple procedures may be needed to ensure that the infection is fully eradicated. Long-term monitoring is often part of the treatment plan, as chronic infections can recur if not properly managed. By addressing both the infection and the structural impact, orthopedic treatment ensures a stronger recovery pathway for patients with stubborn wounds.
Rehabilitation and Recovery in Orthopedic Wound Care
Healing does not stop after the wound closes; rehabilitation is an essential part of orthopedic wound care. Physical therapy plays a major role in restoring mobility, strength, and function, especially if the wound affected muscles or joints. Patients are guided through safe exercises that encourage blood circulation and prevent stiffness. Nutrition is also emphasized, as proteins, vitamins, and minerals are critical for tissue repair. Many patients with non-healing wounds also have underlying conditions such as diabetes or vascular disease, which require close monitoring to prevent setbacks. Orthopedic specialists often work with endocrinologists, nutritionists, and physical therapists to create a holistic recovery plan. Gradual reintegration into daily routines helps patients regain confidence and independence without risking re-injury. Preventive strategies, such as proper footwear for diabetic patients or protective measures for those prone to injuries, are equally important in long-term care. Rehabilitation ensures that patients not only recover from wounds but also reduce the likelihood of future complications.
Innovations in Orthopedic Wound Treatment
The field of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is advancing rapidly with innovative techniques. Regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy, is showing promise in regenerating damaged tissues and improving healing outcomes. 3D-printed implants and scaffolds are also being used to replace or support bone and soft tissue in complex wound scenarios. Smart wound dressings equipped with sensors can monitor moisture levels, detect infection, and send real-time updates to healthcare providers. Minimally invasive surgical techniques allow orthopedic specialists to treat wounds and related structural damage with less trauma and faster recovery times. Additionally, biologically active materials that stimulate cell growth are being introduced as part of advanced wound care. These innovations offer new hope for patients whose wounds previously seemed impossible to heal. As research continues, patients can expect more personalized, efficient, and effective orthopedic solutions for chronic wounds.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Specialist for Non-Healing Wounds
Selecting the right orthopedic specialist is crucial for effective treatment. Patients should look for doctors with specific experience in treating chronic or complex wounds, particularly those linked to orthopedic conditions. Board certification, years of practice, and expertise in wound management are important factors to consider. It is also valuable to choose a specialist who works within a multidisciplinary clinic, ensuring access to vascular, infectious disease, and physical therapy support. During consultations, patients should ask about available treatment options, recovery timelines, and risks associated with different procedures. A good orthopedic specialist not only treats the wound but also educates the patient on preventive care and lifestyle adjustments. Building trust with the medical team creates a supportive environment for long-term healing. With the right specialist, patients can expect improved outcomes and a higher chance of restoring function and mobility after non-healing wounds.
FAQ Section
Q1: What makes orthopedic treatment different from standard wound care?
Orthopedic treatment addresses not only the wound itself but also the underlying musculoskeletal issues that may be preventing healing. This approach is critical when bones, joints, or tendons are involved.
Q2: When should I see an orthopedic doctor for a non-healing wound?
If a wound does not show signs of healing within weeks, or if bone, joint, or deep tissue is exposed, it is time to consult an orthopedic doctor. Chronic pain, swelling, or infection are also warning signs.
Q3: Can orthopedic treatments help with diabetic wounds?
Yes, many diabetic wounds involve structural complications that require orthopedic expertise. Specialists can provide surgical and non-surgical treatments to protect mobility and prevent severe complications.
Q4: Are surgeries always necessary for orthopedic wound care?
Not all cases require surgery. Some patients may benefit from advanced dressings, biologics, or therapies like hyperbaric oxygen. Surgery is usually reserved for severe or infected wounds.
Q5: How long does recovery usually take after orthopedic wound treatment?
Recovery depends on the severity of the wound, overall health, and type of treatment used. Some patients heal within weeks, while others with complex wounds may require months of rehabilitation.