Understanding Non-Healing Wounds
Non-healing wounds are a persistent medical challenge that can significantly impact a patient’s overall health and mobility. Unlike typical wounds that heal within a few weeks, chronic wounds fail to close properly and remain vulnerable to infection, inflammation, and tissue damage. Common causes include diabetes, poor circulation, vascular disorders, prolonged pressure on specific body areas, or underlying orthopedic conditions. These wounds can affect not only the skin but also muscles, bones, and joints, potentially leading to long-term complications if left untreated. Early recognition of warning signs—such as persistent redness, swelling, foul odor, or discharge—is essential to prevent deterioration. Patients and caregivers must remain vigilant, as timely intervention can dramatically improve outcomes. Understanding the factors contributing to non-healing wounds is the first step in developing effective orthopedic treatment strategies.
The Role of Orthopedic Intervention
Orthopedic specialists are uniquely positioned to assess and manage chronic wounds, especially when the wound involves underlying bones or connective tissue. The evaluation process begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination to identify risk factors and possible complications. Diagnostic tools like imaging scans, blood flow studies, and tissue biopsies help uncover structural or systemic issues that may impede healing. Conditions such as osteomyelitis, neuropathy, and deformities in bone or joints require specialized treatment to prevent further deterioration. Orthopedic intervention also focuses on restoring function, mobility, and structural support, ensuring that treatment is not just about healing the wound but also improving overall quality of life. Collaboration with wound care nurses, endocrinologists, and physical therapists ensures a multidisciplinary approach for the best possible outcomes.
Advanced Treatment Approaches
Treatment for non-healing wounds often requires a combination of surgical and non-surgical strategies. Surgical options include debridement, which removes necrotic tissue, and skin grafts or flap surgeries that provide new tissue to aid healing. These procedures restore blood supply and promote tissue regeneration, creating optimal conditions for recovery. Orthopedic devices, such as braces, casts, or offloading supports, reduce pressure on the affected area, facilitating proper healing. Minimally invasive techniques, including laser therapy or tissue regeneration therapy, are increasingly used to stimulate the body’s natural repair processes without extensive surgical intervention. The choice of treatment depends on wound size, location, depth, and the patient’s overall health status. Personalized treatment plans ensure that patients receive the most effective combination of therapies, supporting both short-term recovery and long-term wellness.
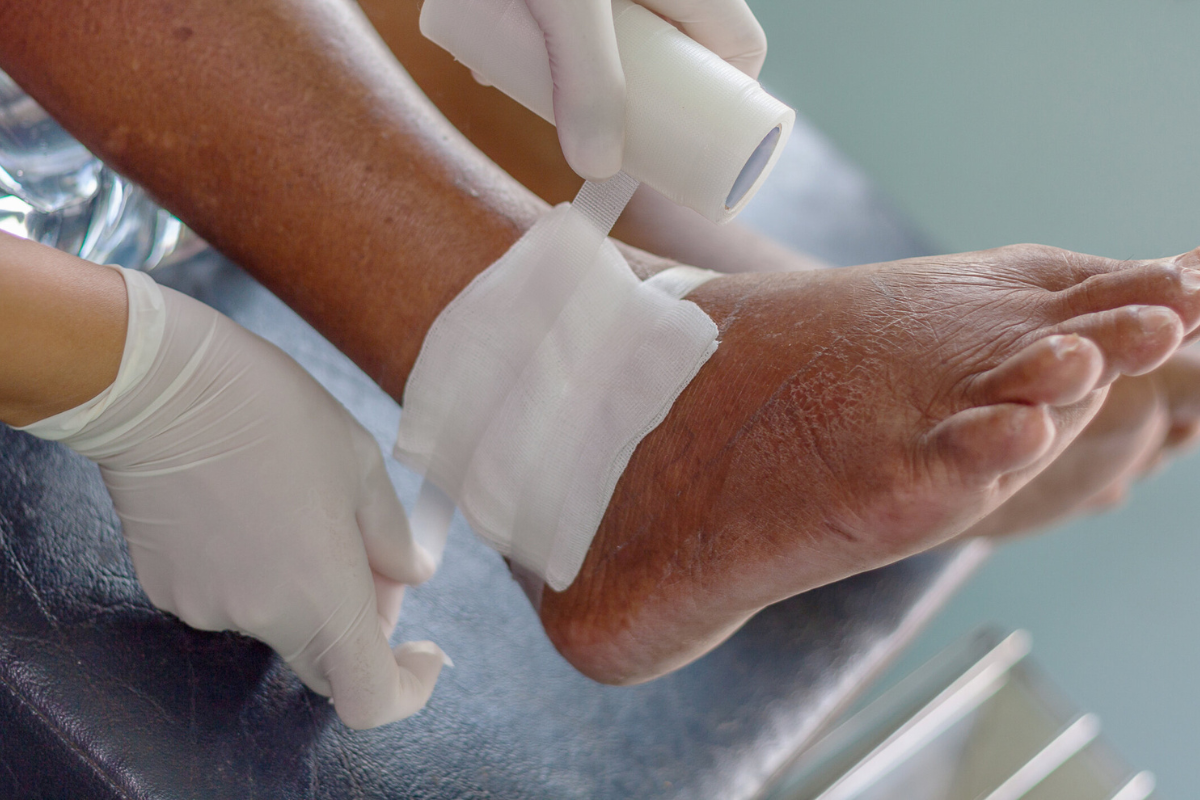
Wound Care Management in Orthopedics
Effective wound care is a cornerstone of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Modern wound dressings use advanced materials that support tissue repair, manage moisture levels, and prevent infections. Options may include hydrocolloid, foam, antimicrobial, or gel-based dressings tailored to the specific wound type. Infection control is particularly important, as chronic wounds are highly susceptible to bacterial contamination, which can slow healing or trigger complications. Orthopedic specialists may prescribe systemic or topical antibiotics depending on the wound’s condition and lab results. Pain management is also critical, as chronic wounds can cause persistent discomfort and impact daily activities. Strategies include localized anesthetics, non-opioid pain relievers, and targeted therapies designed to minimize discomfort while supporting tissue repair. Patient education on proper dressing techniques, hygiene, and monitoring is essential for effective wound management and preventing further complications.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Physical therapy and rehabilitation are vital for patients recovering from non-healing wounds. Targeted exercises improve circulation, strengthen surrounding muscles, and reduce pressure on vulnerable areas, which enhances the healing process. Rehabilitation also helps maintain joint mobility, prevents stiffness, and reduces the risk of further orthopedic complications. Customized therapy programs are tailored to individual patient needs, ensuring safe and sustainable progress. Therapists teach strategies to prevent wound recurrence, including proper posture, offloading techniques, and adaptive movement patterns. Consistent rehabilitation, combined with medical care, supports holistic recovery, enabling patients to regain independence, mobility, and confidence. Integrating rehabilitation early in the treatment plan often leads to better long-term outcomes.
Lifestyle and Holistic Considerations
Lifestyle factors play a significant role in the healing process. Nutrition is critical, as adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals support tissue repair and immune function. Managing underlying conditions such as diabetes, obesity, or circulatory disorders is equally important for effective wound healing. Patients are encouraged to monitor glucose levels, improve blood flow, and adhere to recommended medical regimens. Adequate hydration, rest, and stress management also contribute to optimal recovery by allowing the body to focus on tissue repair. Early recognition of any changes in the wound, such as increased redness, swelling, or unusual discharge, allows for prompt intervention. Educating patients and caregivers empowers them to take an active role in recovery and prevent recurrence of chronic wounds.
Technological Innovations in Orthopedic Wound Treatment
Recent advancements in orthopedic care have revolutionized the treatment of non-healing wounds. Stem cell therapy, growth factor treatments, and biologics promote tissue regeneration and accelerate healing. Advanced imaging, including 3D modeling, assists surgeons in planning precise interventions to optimize outcomes. Telemedicine allows patients to receive remote monitoring and guidance, ensuring continuous care without frequent hospital visits. Wearable devices can track pressure and circulation to help prevent worsening of chronic wounds. These technologies complement traditional orthopedic methods, offering patients innovative options that improve healing speed and overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does it typically take for an orthopedic-treated wound to heal?
Healing time varies depending on the wound’s severity, underlying conditions, and treatment method. Some wounds may take weeks, while others require several months of comprehensive care.
Can non-healing wounds lead to more serious orthopedic complications?
Yes. If left untreated, chronic wounds can lead to infections in bones and joints, decreased mobility, and long-term structural problems.
Are there non-surgical options to promote healing?
Absolutely. Offloading devices, advanced wound dressings, physical therapy, and targeted medications can often support healing without surgical intervention.
What role does nutrition play in orthopedic wound recovery?
Proper nutrition provides essential building blocks for tissue repair, immune function, and overall healing. Proteins, vitamins, and minerals are particularly important.
How often should a patient visit an orthopedic specialist for chronic wounds?
Frequency depends on wound severity and treatment method. Regular check-ups, often weekly or biweekly, ensure proper monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans.