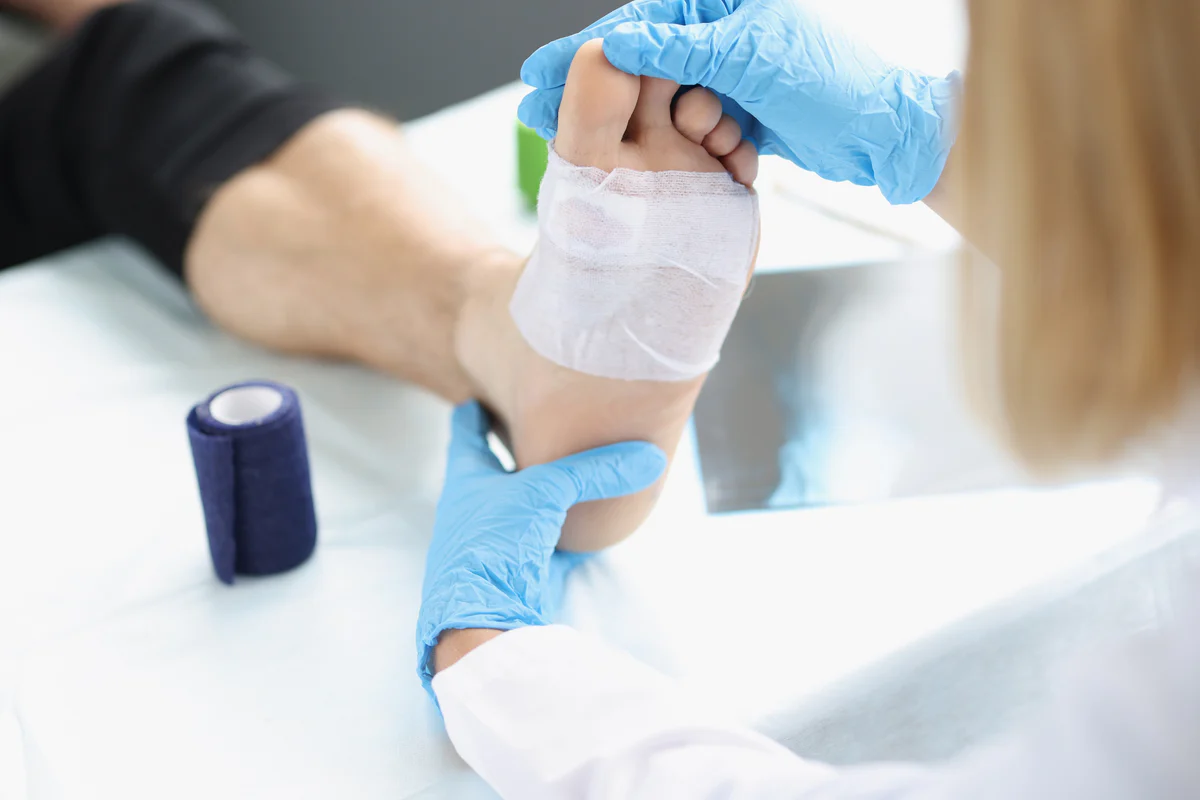
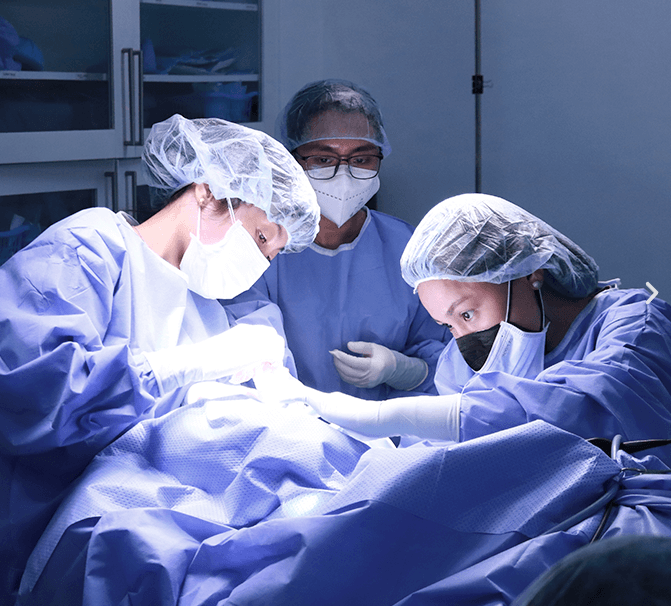
Forefoot ulcers are open sores or wounds that develop on the front part of the foot, typically affecting the toes or the ball of the foot. These ulcers often occur due to repeated pressure, friction, or trauma, which can damage the skin and underlying tissues. Individuals with diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, or poor circulation are especially at risk, as their feet may not heal efficiently, and nerve damage can prevent them from detecting pain or discomfort. Early signs of forefoot ulcers include redness, swelling, blistering, or persistent soreness in localized areas. If left untreated, these ulcers can lead to serious complications, including infections, cellulitis, or osteomyelitis, which is a bone infection. Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers addresses not only the wound itself but also the mechanical issues that contribute to ulcer formation. Understanding these causes and early warning signs is essential for effective management and prevention.
The Role of Orthopedic Treatment
Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers focuses on correcting structural and biomechanical factors that contribute to ulcer formation. Unlike standard wound care, orthopedic approaches aim to reduce pressure on vulnerable areas, improve foot alignment, and enhance mobility. A multidisciplinary strategy, often combining podiatry, physical therapy, and orthopedic care, tends to produce the best results. Orthopedic interventions redistribute weight across the foot to prevent stress on ulcer-prone areas. They also provide support for weakened muscles and tendons, which may otherwise worsen pressure points. Evaluating a patient’s gait, foot structure, and daily activity is crucial for creating a customized treatment plan. By addressing both the ulcer and its underlying causes, orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers provides a more comprehensive and long-lasting solution.
Orthopedic Devices and Tools
A variety of orthopedic devices are commonly used to treat and prevent forefoot ulcers. Custom orthotics are designed to fit the unique contours of a patient’s foot, helping to offload pressure from high-risk areas. Specialized footwear, such as diabetic shoes or padded insoles, provides extra protection while reducing friction. Braces, padding, and other supportive devices help stabilize joints and evenly distribute weight across the forefoot. Advances in technology have produced lightweight, durable materials that maximize comfort and healing. Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers often combines multiple devices to provide the best results. Regular monitoring and adjustments ensure these tools remain effective as the foot changes over time. Consistent use of these orthopedic devices is critical for preventing further damage and promoting healing.
Non-Surgical Treatment Approaches
Non-surgical orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers emphasizes conservative methods to support healing while minimizing risks. Wound care techniques such as debridement remove dead tissue, while advanced dressings promote faster recovery. Pressure relief strategies, including the use of orthotics and specialized footwear, reduce strain on the affected area. Physical therapy can improve foot mobility, strengthen muscles, and correct gait abnormalities that contribute to ulcers. Controlling infections is also essential, with careful monitoring to detect bacterial growth or inflammation. Non-surgical approaches are particularly effective for mild to moderate ulcers, offering safe, low-risk options for patients. When combined with patient education and lifestyle adjustments, these strategies enhance the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
In severe or persistent cases, surgical intervention may be necessary as part of orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers. Surgery is usually recommended when ulcers fail to respond to conservative care or when significant tissue damage, infection, or bone involvement occurs. Common procedures include tendon release, bone realignment, and skin grafting to close chronic wounds. After surgery, patients typically require supportive footwear, orthotics, and physical therapy to ensure proper healing. Recovery time varies depending on the procedure and the patient’s overall health, making post-surgical care essential. Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers through surgery can restore function, reduce pain, and prevent future complications. Close collaboration with an orthopedic specialist ensures the surgical plan meets each patient’s unique needs.
Lifestyle and Daily Management
Daily care and lifestyle choices are key to the success of orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers. Regular foot hygiene, including cleaning, moisturizing, and inspecting the feet, prevents infections and irritation. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the forefoot, lowering ulcer risk. Activity modifications, such as avoiding high-impact exercises or prolonged standing, protect vulnerable areas. Nutrition also supports healing, with protein-rich foods and hydration aiding tissue repair. Educating patients on proper use of orthotics, footwear, and early detection of new ulcers empowers them to actively participate in their recovery. Consistent daily management enhances the long-term benefits of orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers and helps prevent recurrence.
Preventing Recurrence
Preventing forefoot ulcers from returning is a major focus of orthopedic treatment. Ongoing use of custom orthotics and protective footwear reduces stress on high-risk areas. Regular check-ups with podiatrists or orthopedic specialists help detect issues before they develop into ulcers. Patient education is crucial, teaching individuals to recognize warning signs, maintain proper foot hygiene, and follow prescribed care routines. Adjusting orthotics and footwear over time ensures continued support as the foot changes. Lifestyle measures, including weight management, safe exercise, and controlling underlying conditions like diabetes, further minimize ulcer risk. Combining orthopedic interventions with proactive self-care allows patients to maintain mobility, prevent future ulcers, and improve overall foot health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What causes forefoot ulcers to develop?
Forefoot ulcers develop due to pressure, friction, poor circulation, and underlying conditions like diabetes or neuropathy. Repeated stress on vulnerable areas of the foot damages the skin and underlying tissue.
How effective is orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers compared to traditional care?
Orthopedic treatment addresses both the ulcer and the mechanical causes of tissue damage. This makes it more comprehensive than standard wound care, promoting faster healing and reducing recurrence.
Can custom orthotics completely prevent ulcers?
Custom orthotics greatly reduce pressure on high-risk areas but cannot guarantee full prevention. Combining orthotics with foot care, lifestyle changes, and monitoring produces the best results.
How long does it take for a forefoot ulcer to heal with orthopedic care?
Healing times vary depending on ulcer severity, the patient’s overall health, and adherence to treatment. Mild ulcers may heal in a few weeks, while severe cases can take several months.
Are there risks associated with surgical treatment for forefoot ulcers?
Surgery carries risks such as infection, delayed healing, or anesthesia complications. However, with proper post-operative care, surgical intervention can be highly effective in restoring foot function and preventing further ulcers.