Understanding Green Roof Systems
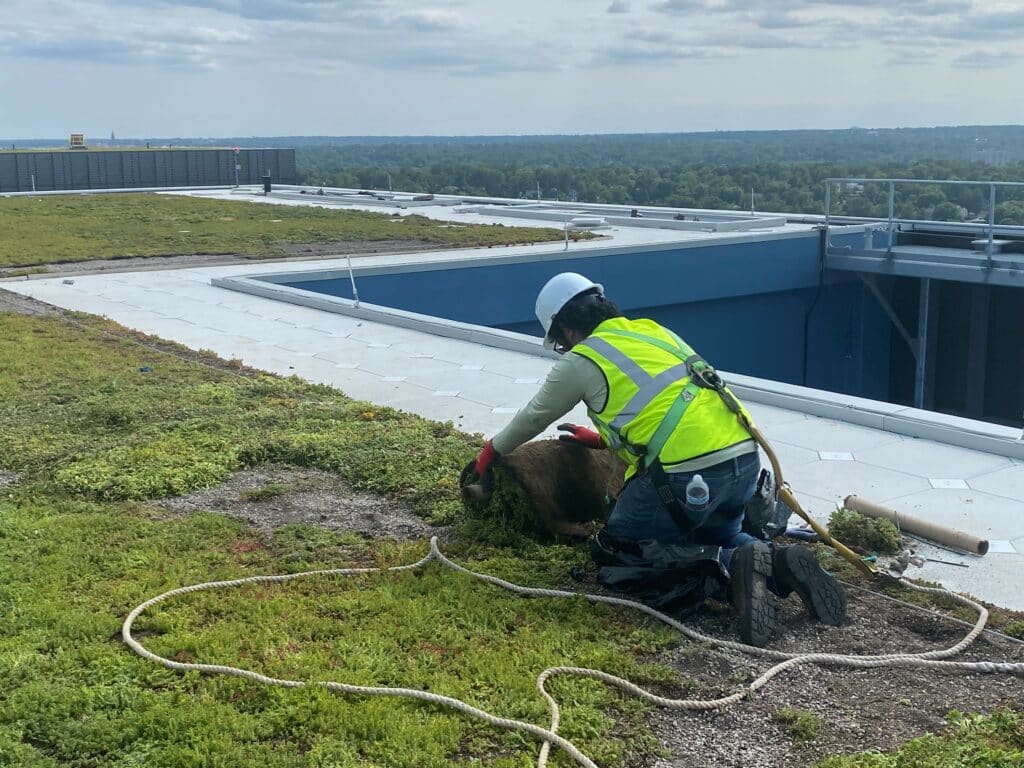
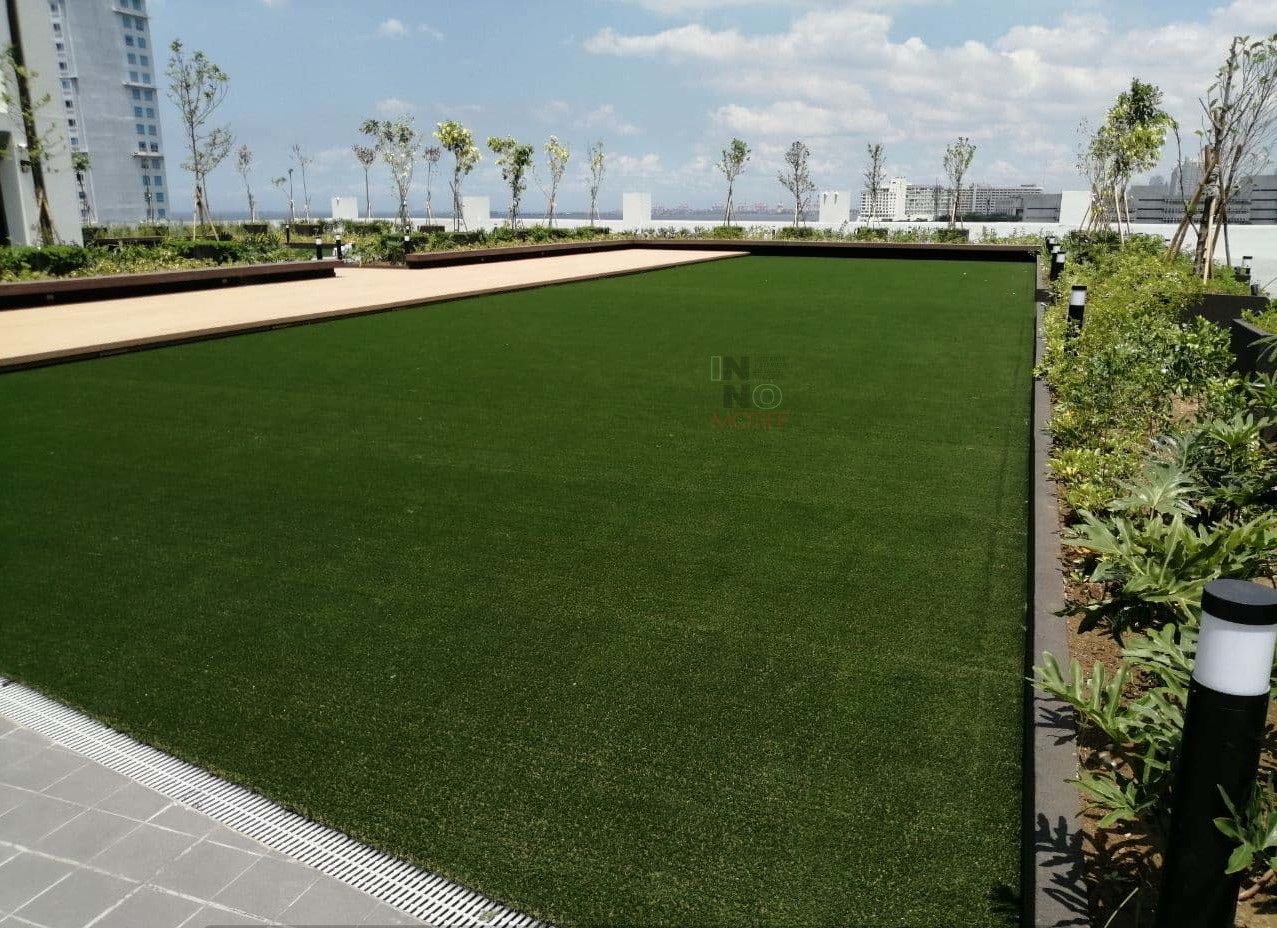
A green roof system is a sustainable solution that integrates vegetation into rooftop spaces, providing both aesthetic and environmental benefits. Unlike traditional roofs, a green roof system incorporates layers such as waterproofing, drainage, substrate, and plants, allowing buildings to interact with natural elements. There are two primary types of green roofs: intensive and extensive. Intensive green roofs are deeper, can support a wider variety of plants, and are often accessible as recreational spaces. Extensive green roofs are lighter, require less maintenance, and are ideal for energy efficiency and stormwater management. The selection of a green roof system depends on building structure, climate, and intended use. Installing a green roof system requires careful planning to ensure the structure can support additional weight and to choose the right vegetation for durability and environmental impact.
Environmental Benefits of Green Roof Systems
Green roof systems play a vital role in improving urban environmental quality. One of their most notable contributions is reducing urban heat islands by cooling the surrounding air and reflecting less heat than traditional rooftops. They also improve air quality by capturing airborne pollutants and carbon dioxide, contributing to cleaner and healthier urban areas. Green roof systems manage stormwater by absorbing rainfall, reducing runoff, and decreasing the burden on urban drainage systems. These systems can support biodiversity by providing habitats for birds, insects, and small wildlife in densely populated areas. The vegetation layers act as natural insulation, helping regulate indoor temperatures and reducing energy consumption. In areas with frequent rainfall or strong sunlight, green roof systems protect buildings from extreme weather effects. Integrating greenery into cities not only enhances aesthetics but also promotes ecological balance in urban planning.
Economic Advantages
Investing in a green roof system can yield long-term economic benefits for property owners. One of the key advantages is energy efficiency, as the vegetation layer provides natural insulation, reducing heating and cooling costs. Green roofs can extend the lifespan of roofing materials by shielding them from direct sunlight, wind, and temperature fluctuations. Property values can increase as sustainability becomes a selling point and tenants or buyers are attracted to eco-friendly buildings. Green roof systems may qualify for tax incentives, rebates, or grants, depending on local government programs, further offsetting installation costs. Additionally, energy savings and reduced maintenance costs contribute to a positive return on investment over time. Businesses and residential complexes can also benefit from enhanced reputation and public perception by implementing visible sustainable practices. Choosing a green roof system is not just an environmental decision; it is a financially strategic one.
Health and Lifestyle Benefits
The presence of a green roof system contributes significantly to the well-being of occupants and communities. Access to green spaces has been linked to reduced stress levels, improved mental health, and increased productivity in work environments. Green roofs also act as sound barriers, reducing noise pollution from traffic and urban activity. Recreational areas can be incorporated into intensive green roof systems, allowing residents or employees to enjoy outdoor spaces even in high-density cities. The greenery can improve indoor air quality by reducing airborne dust and pollutants, providing a healthier environment. Plants on green roofs can filter toxins and create a calming atmosphere, which is beneficial for people living in busy urban areas. Overall, incorporating a green roof system enhances quality of life while promoting sustainable urban living.
Design and Installation Considerations
Installing a green roof system requires careful design to ensure effectiveness and longevity. Structural assessment is crucial to determine if the building can bear the additional weight of soil, plants, and water. Plant selection should match the local climate, sunlight exposure, and maintenance capabilities. Drainage systems are essential to prevent water accumulation and potential leaks, ensuring the roof remains functional and safe. Green roof systems also require waterproofing layers to protect the building from moisture damage. Maintenance plans should include irrigation, fertilization, pruning, and seasonal checks to sustain healthy vegetation. Designing a green roof system involves balancing aesthetics, functionality, and long-term sustainability.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite their benefits, green roof systems face certain challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation. Common issues include water leakage, root penetration, and drainage blockages. These problems can be mitigated through careful design, professional installation, and the use of high-quality materials. Regular maintenance is crucial to prevent plant overgrowth, soil erosion, and pest infestations. Cost may be a concern initially, but the long-term energy savings and extended roof lifespan compensate for upfront investments. Ensuring that the roof structure meets load-bearing requirements avoids potential structural damage. With proper planning, monitoring, and maintenance, these challenges can be transformed into manageable aspects of sustainable roofing. A proactive approach ensures that a green roof system remains efficient and durable for decades.
Innovations in Green Roof Technology
Green roof systems continue to evolve with innovative solutions that enhance efficiency and ease of maintenance. Smart irrigation systems automatically monitor moisture levels and provide water as needed, reducing manual effort and water waste. Modular green roof systems offer pre-planted trays that simplify installation and replacement. Some green roof systems are now integrated with solar panels, combining energy generation with natural cooling benefits. Advanced sensors can track plant health, drainage performance, and structural integrity, making management more data-driven. Eco-friendly materials and lightweight substrates allow for broader applications, including retrofitting older buildings. These technological advancements make green roof systems increasingly accessible, efficient, and adaptable for urban spaces.
Regulatory and Incentive Landscape
Local regulations play a significant role in the adoption of green roof systems. Building codes may require specific structural assessments or permits before installation. Governments often provide incentives, grants, or rebates for sustainable roofing solutions, making green roof systems more financially attractive. Sustainability certifications, such as LEED, can also recognize buildings with green roofs, enhancing market appeal. Urban planning initiatives encourage green infrastructure to improve environmental quality and resilience. Awareness of regulatory requirements ensures compliance and smooth project execution. Incentives and certifications act as additional motivators for developers to invest in green roof systems. Incorporating these systems aligns with both environmental goals and legal frameworks.
Green Roof System in Action
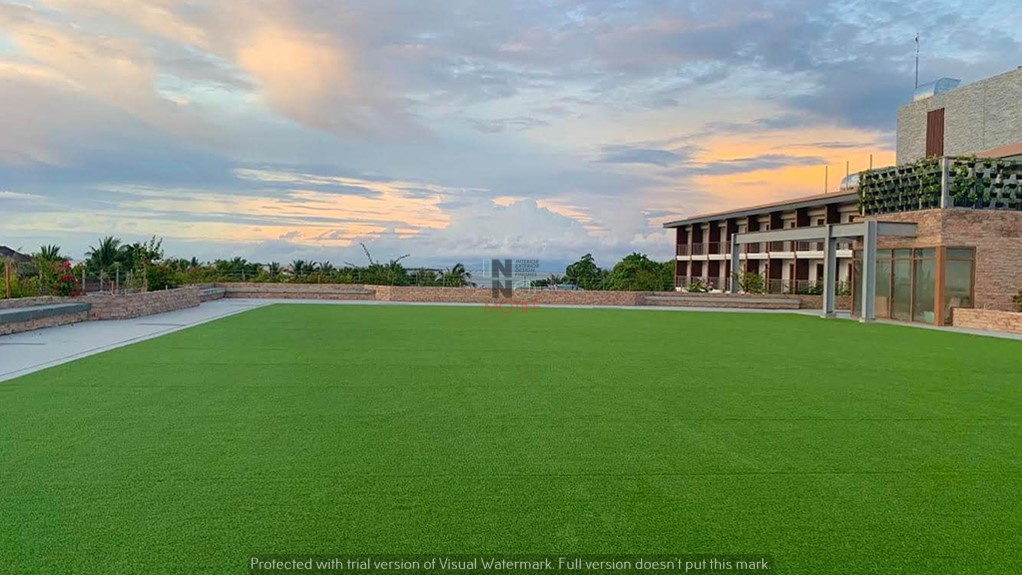
Green roof systems can be adapted for a wide range of urban and industrial applications. Commercial buildings benefit from reduced energy costs, stormwater management, and enhanced corporate image. Residential complexes gain recreational areas, improved aesthetics, and increased property value. Industrial facilities can use green roofs to reduce heat absorption, manage rainwater, and improve sustainability metrics. Cities around the world are implementing green roof systems in public infrastructure, such as schools, libraries, and transport hubs. Green roofs can thrive in different climates, with careful plant selection and maintenance strategies tailored to local conditions. The versatility of a green roof system makes it an essential element in sustainable urban design.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- How long does it take to install a green roof system? Installation timelines vary depending on the building size and type of green roof system, but most projects take several weeks to a few months.
- What maintenance is required for a green roof system? Regular maintenance includes watering, fertilization, pruning, checking drainage, and inspecting the waterproofing layer to ensure plant and roof health.
- Can green roofs be installed on existing buildings? Yes, with proper structural assessment and modifications, existing buildings can support both intensive and extensive green roof systems.
- What is the average cost of installing a green roof system? Costs depend on size, type, plant selection, and structural modifications, but long-term energy savings and roof longevity often justify the investment.
- Do green roofs help in reducing energy bills? Absolutely. By providing natural insulation, green roof systems reduce heating and cooling demands, leading to lower energy expenses.
Takeaway
A green roof system is more than a design trend; it is a sustainable solution that delivers environmental, economic, and lifestyle benefits. From reducing energy consumption and managing stormwater to creating healthier urban spaces, green roof systems contribute to long-term building performance and occupant well-being. Innovations in technology and supportive regulatory frameworks make it easier than ever for property owners to invest in green roofs. By carefully planning design, installation, and maintenance, green roof systems can transform urban landscapes into sustainable, vibrant, and resilient environments.