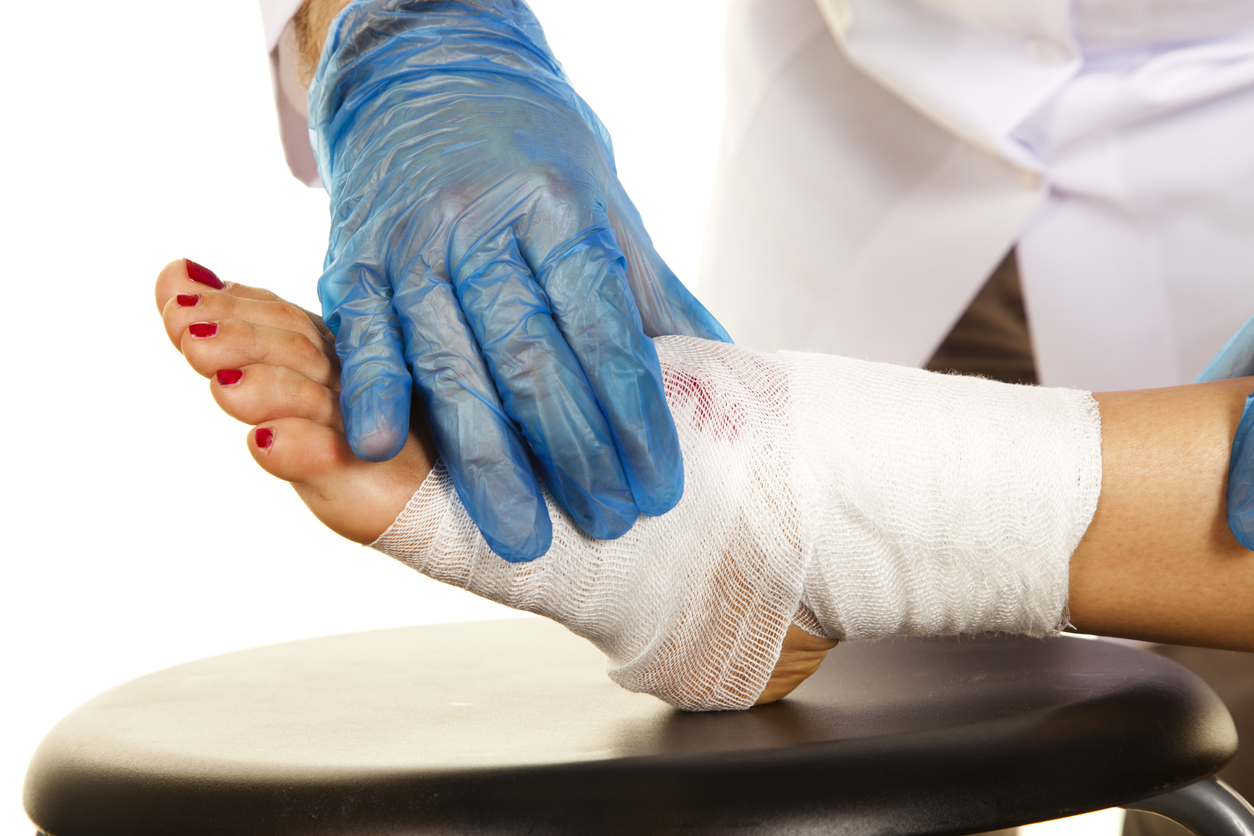
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common and serious complication of diabetes, affecting up to 15% of people with diabetes at some point in their lives. These ulcers are caused by a combination of factors, including nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation (peripheral artery disease), which limit the foot’s ability to heal. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can impair the immune response and reduce the skin’s ability to fight off infections. As a result, even minor injuries to the feet can lead to painful ulcers that are slow to heal and prone to infection. Managing these ulcers is critical to preventing severe complications such as limb amputation.
Understanding the Impact of Diabetes on Foot Health
Diabetes affects the feet in multiple ways. Nerve damage, or neuropathy, reduces sensation in the feet, making it harder for individuals to detect injuries or signs of infection early on. This lack of sensation can lead to unnoticed trauma and ulcers developing without immediate awareness. Additionally, diabetes can cause poor blood circulation, further compromising the healing process. High blood sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels, restricting the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the feet and making wounds slow to heal. Recognizing the symptoms of diabetic foot ulcers—such as redness, swelling, pain, and discharge—can prompt timely treatment to prevent worsening conditions.
Orthopedic Approaches to Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Debridement and Cleaning
The first step in treating diabetic foot ulcers is the removal of dead or infected tissue, a process known as debridement. This helps prevent further infection and prepares the ulcer for healing. Methods of debridement include sharp debridement, where a healthcare professional uses a scalpel or scissors to cut away dead tissue, and enzymatic debridement, which involves applying an enzyme to dissolve dead tissue naturally. Autolytic debridement, which uses the body’s natural processes to clean the ulcer, can also be effective in certain cases. These methods are essential for creating an optimal environment for healing.
Pressure Offloading Techniques
To prevent additional damage to diabetic foot ulcers, it’s crucial to reduce the pressure on the affected area. Custom foot orthotics, diabetic shoes, and braces are commonly used to redistribute weight and provide support, helping to protect the ulcer from further trauma. Total contact casting, a technique that encases the foot in a rigid, padded cast, allows patients to walk without bearing weight on the affected foot, promoting healing. Removable cast walkers and pneumatic walkers also offer support while allowing mobility without applying pressure to the ulcer. These techniques are especially beneficial for ulcers that have not responded to less intensive treatments.
Wound Care Management
Effective wound care is vital to prevent infection and promote healing in diabetic foot ulcers. This includes keeping the ulcer clean and moist using appropriate dressings. Hydrocolloid dressings can create a barrier that protects the wound and absorbs excess fluid, facilitating a clean healing environment. Antimicrobial dressings may be used to combat bacteria and reduce the risk of infection. It’s also important to regularly change dressings to monitor the ulcer’s progress and ensure it is healing properly. This comprehensive approach, coupled with appropriate hygiene practices, is crucial to managing diabetic foot ulcers effectively.
Management of Underlying Conditions
Managing diabetes itself is key to preventing foot ulcers and supporting healing once they occur. Keeping blood sugar levels under control through diet, exercise, and medication is critical in reducing the risk of ulcer development and promoting quicker healing. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat or prevent infection in more severe cases. Antiseptic treatments can also be used to manage infections and promote healing. Addressing comorbidities such as hypertension and high cholesterol can further support overall foot health and prevent complications related to poor circulation.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing diabetic foot ulcers by improving blood flow and foot function. Exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the foot and ankle, as well as enhancing circulation, can be beneficial. Regular check-ups are essential to monitor ulcer healing and adjust treatments as necessary. Patient education is a key component, helping individuals understand the importance of foot care, early detection of issues, and proper use of orthopedic devices. With proper guidance, patients can regain mobility and prevent future ulcers.
Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Routine follow-up care is vital in monitoring the healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Healthcare providers assess the ulcer’s progress, ensuring it is healing properly and not worsening. Signs of complications such as infection—indicated by increased redness, swelling, pain, or pus—require immediate medical attention. Regular foot exams help detect any new ulcers or changes in the skin that could signal a need for intervention. By staying vigilant and proactive, individuals with diabetes can manage their foot health more effectively and reduce the risk of severe complications.
FAQ
- What should I do if my diabetic foot ulcer does not seem to heal? If a diabetic foot ulcer does not show signs of healing after a few weeks, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Non-healing ulcers can indicate infection or other complications that need professional treatment.
- How can I prevent foot ulcers if I have diabetes? Preventing foot ulcers involves keeping blood sugar levels under control, practicing good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and regularly inspecting your feet for cuts or signs of infection. Avoid walking barefoot and use cushioned insoles or orthotic shoes to reduce pressure on the feet.
- Are there specific foot exercises that can help manage diabetic foot ulcers? Yes, foot exercises can improve circulation and strength in the foot and ankle, which helps in managing diabetic foot ulcers. These exercises include toe curls, ankle rotations, and weight shifts. Consult a physical therapist for a tailored exercise program.
- When should I consider surgery for a diabetic foot ulcer? Surgery might be considered if an ulcer is deep, severe, or associated with an infection that cannot be managed with medication alone. The goal is to remove infected tissue or improve blood flow to the area. Your healthcare provider will determine if surgery is necessary based on the ulcer’s condition and overall health.
- How can I find a specialist who treats diabetic foot ulcers? To find a specialist, consult your primary care physician or a podiatrist. They can refer you to a healthcare provider who specializes in diabetic foot care. Hospitals and diabetes centers may also offer specialized clinics for managing diabetic foot ulcers.